 English
English Russian
Russian Español
Español Français
Français Deutsch
Deutsch हिन्दी
हिन्दी
 සිංහල
සිංහල
 中文
中文
 日本語
日本語
What Is Thermal Throttling and Why Does It Happen?
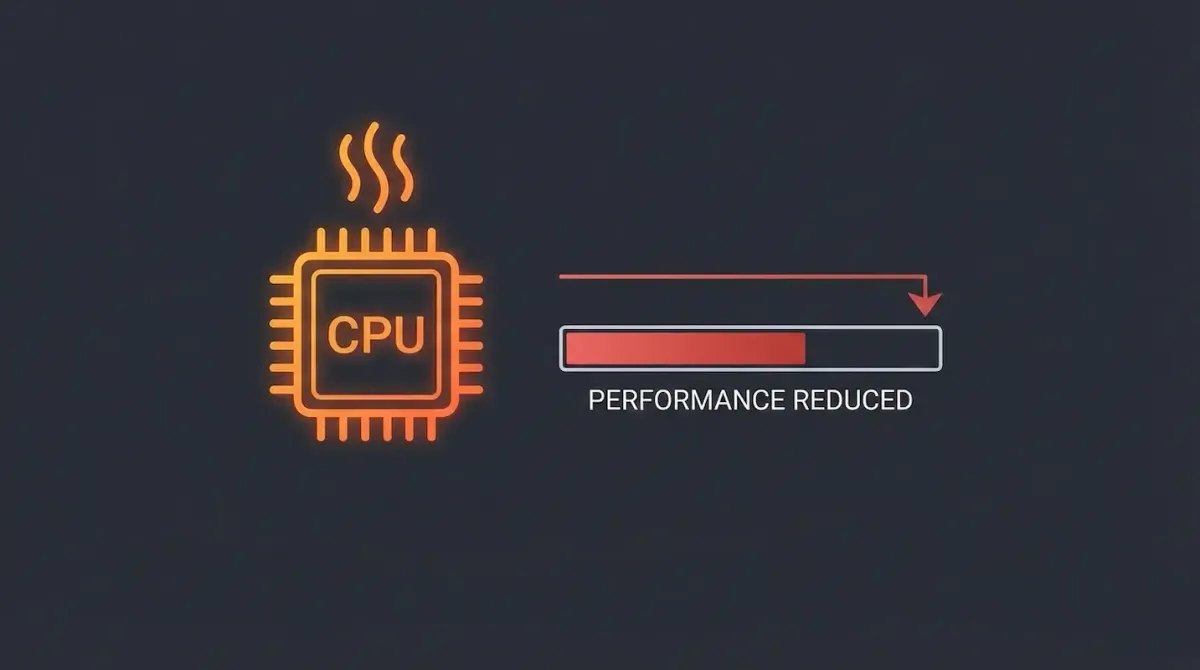
You buy a powerful gaming PC or a premium laptop expecting smooth performance. At first, everything feels perfect. Games run at high frame rates, applications open instantly, and the system feels fast. Then, after a few minutes, performance suddenly drops. Frame rates fall sharply, fans become extremely loud, and the entire system feels slow.
This behavior is almost always caused by thermal throttling.
Thermal throttling is one of the most common reasons even expensive computers fail to deliver consistent performance. Understanding how it works can help you fix the problem without upgrading your hardware.
What Is Thermal Throttling?
Thermal throttling is a built-in hardware protection mechanism used by both CPUs and GPUs.
Every processor has a maximum safe operating temperature. For most modern processors from companies like Intel and AMD, this limit is close to 100°C for CPUs and around 85°C for GPUs.
When a processor reaches this temperature, it automatically reduces its clock speed to prevent damage. Lower clock speeds generate less heat, allowing the chip to cool down.
In simple terms, your computer slows itself down to avoid overheating and permanent hardware damage.
Why Thermal Throttling Happens
Thermal throttling occurs when heat builds up faster than your cooling system can remove it. This usually happens due to a few common reasons.
Dust Buildup Inside the System
Dust is one of the biggest enemies of cooling performance. Over time, dust accumulates on fans, vents, and heatsinks. This layer blocks airflow and traps heat inside the system.
Even if your fans are spinning at full speed, clogged airflow prevents heat from escaping efficiently.
Old or Dried Thermal Paste
Thermal paste sits between the processor and the cooler and helps transfer heat. After two or three years, this paste often dries out and loses effectiveness.
This issue is especially common in laptops, where compact cooling designs already struggle to dissipate heat. Replacing old thermal paste is one of the most effective ways to reduce temperatures.
Poor Airflow Design
Desktop PCs rely on proper airflow. Cool air must enter the case while hot air exits. If a case has too few intake or exhaust fans, hot air circulates inside instead of being pushed out.
Laptops can also suffer from airflow problems when vents are blocked by dust, fabric, or soft surfaces like beds.
Common Signs of Thermal Throttling
There are clear warning signs that indicate your system is throttling.
- Games run smoothly at first, then suddenly stutter or drop frames
- Performance improves briefly after closing applications, then drops again
- Fans stay at maximum speed for long periods
- Laptop keyboards or palm rests become uncomfortably hot
Monitoring tools such as HWMonitor or built-in utilities can confirm whether temperatures spike just before performance drops.
How to Fix Thermal Throttling Without Upgrading Hardware
Before spending money on new parts, try these effective fixes.
Clean the System Thoroughly
Compressed air can remove years of dust buildup. Power off the system, open the case if possible, and clean fans, heatsinks, and vents.
When cleaning, hold fan blades in place to prevent them from spinning too fast, which can damage components.
Apply New Thermal Paste
Replacing thermal paste is inexpensive and highly effective. A fresh application of quality paste such as Arctic MX-6 can lower temperatures by 10 to 15 degrees Celsius.
This is especially important for systems that are more than three years old.
Undervolting the CPU or GPU
Modern processors often run with more voltage than necessary. Tools like Intel XTU or AMD Ryzen Master allow you to reduce voltage safely.
Lower voltage means lower heat output, often without reducing performance. This method is popular among laptop users dealing with thermal limits.
Improve Airflow
For desktops, adding or repositioning case fans can dramatically improve cooling. Ensure cool air enters from the front or bottom and hot air exits from the rear or top.
For laptops, always use the device on a hard surface and keep vents unobstructed.
Conclusion
Thermal throttling is not a defect. It is a safety feature designed to protect your hardware from overheating. However, frequent throttling is a clear sign that your cooling system needs attention.
Regular cleaning, fresh thermal paste, and minor tuning can restore lost performance and keep your system running fast and stable. In most cases, proper maintenance is all it takes to turn a sluggish system back into a powerful one.
Source - intel.com , tomshardware.com






